JavaScript must be enabled in order to use this site.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser and refresh the page.
Oct 16, 2017 To create a Kerberos.keytab file for a host computer that isn't running the Windows operating system, you must map the principal to the account and set the host principal password. Use the active directory User and computers snap-in to create a user account for a service on a computer that is not running the Windows operating system. Create a service account (basically a user account). Run Ktpass.exe to generate the keytab file. Test the keytab file (optional step yet an invaluable time saver sometimes). Ktpass is the tool that does all the magic. If it is run correctly then it generates a keytab file after configuring all the SPN (Service Principal Name) mappings.
This is the documentation for Cloudera Enterprise 5.11.x. Documentation for other versions is available at Cloudera Documentation.
If your version of Kerberos does not support the Kerberos -norandkey option in the xst command, or if you must usekadmin because you cannot use kadmin.local, then you can use the following procedure to create Kerberos keytab files. Using the-norandkey option when creating keytabs is optional and a convenience, but it is not required.
Important:For both MRv1 and YARN deployments:On every machine in your cluster, there must be a keytab file for the hdfs user and a keytab file for the mapred user. The hdfs keytab file must contain entries for the hdfs principal and an HTTP principal, and the mapred keytab file must contain entries for the mapred principal and an HTTP principal. On each respective machine, the HTTP principal will be the same in both keytabfiles.
In addition, for YARN deployments only:On every machine in your cluster, there must be a keytab file for the yarn user. The yarn keytab file must contain entries for the yarn principal and an HTTPprincipal. On each respective machine, the HTTP principal in the yarn keytab file will be the same as the HTTP principal in the hdfs and mapred keytab files.
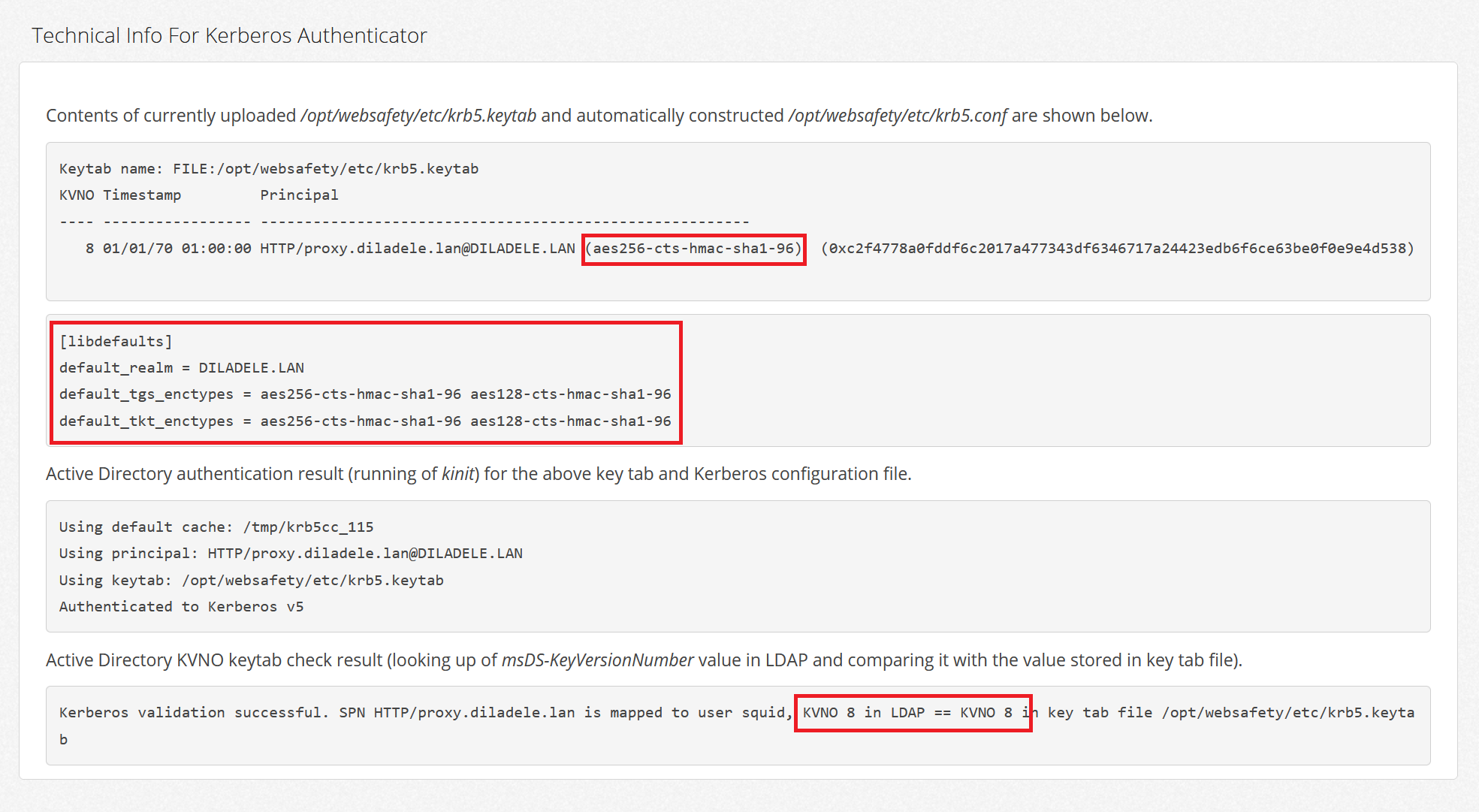
Generate Keytab File From Active Directory
For instructions, see To create the Kerberos keytab files.
Note:
These instructions illustrate an example of creating keytab files for MIT Kerberos. If you are using another version of Kerberos, refer to your Kerberos documentation for instructions.You can use either kadmin or kadmin.local to run these commands.
To create the Kerberos keytab files
Do the following steps for every host in your cluster, replacing the fully.qualified.domain.name in the commands with the fully qualified domain name ofeach host:
- Create the hdfs keytab file, which contains an entry for the hdfs principal. This keytab file is used for the NameNode,Secondary NameNode, and DataNodes.
- Create the mapred keytab file, which contains an entry for the mapred principal. If you are using MRv1, the mapred keytab file is used for the JobTracker and TaskTrackers. If you are using YARN, the mapred keytab file is used for the MapReduce Job HistoryServer.
- YARN only: Create the yarn keytab file, which contains an entry for the yarn principal. Thiskeytab file is used for the ResourceManager and NodeManager.
- Create the http keytab file, which contains an entry for the HTTP principal.
- Use the ktutil command to merge the previously-created keytabs:
This procedure creates three new files: hdfs.keytab, mapred.keytab and yarn.keytab. Thesefiles contain entries for the hdfs and HTTP principals, the mapred and HTTPprincipals, and the yarn and HTTP principals respectively.
- Use klist to display the keytab file entries. For example, a correctly-created hdfs keytab file should look something likethis:
- To verify that you have performed the merge procedure correctly, make sure you can obtain credentials as both the hdfs and HTTP principals using the single merged keytab:
If either of these commands fails with an error message such as 'kinit: Key table entry not found while getting initial credentials', then something hasgone wrong during the merge procedure. Go back to step 1 of this document and verify that you performed all the steps correctly.
- To continue the procedure of configuring Hadoop security in CDH 5, follow the instructions in the section To deploy the Kerberos keytab files.
Applies To: Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows 8
Configures the server principal name for the host or service in Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) and generates a .keytab file that contains the shared secret key of the service. The .keytab file is based on the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) implementation of the Kerberos authentication protocol. The Ktpass command-line tool allows non-Windows services that support Kerberos authentication to use the interoperability features provided by the Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) service. This topic applies to the operating system versions designated in the Applies To list at the beginning of the topic.

For examples of how this command can be used, see Examples.
Syntax
Parameters
Parameter | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
/out <FileName> | Specifies the name of the Kerberos version 5 .keytab file to generate.
| ||
/princ <PrincipalName> | Specifies the principal name in the form host/computer.contoso.com@CONTOSO.COM. Warning This parameter is case sensitive. See Remarks for more information. | ||
/mapuser <UserAccount> | Maps the name of the Kerberos principal, which is specified by the princ parameter, to the specified domain account. | ||
/mapop {add|set} | Specifies how the mapping attribute is set.
| ||
{-|+}desonly | DES-only encryption is set by default.
Important Beginning with Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows does not support DES by default. | ||
/in <FileName> | Specifies the .keytab file to read from a host computer that is not running the Windows operating system. | ||
/pass {Password|*|{-|+}rndpass} | Specifies a password for the principal user name that is specified by the princ parameter. Use '*' to prompt for a password. | ||
/minpass | Sets the minimum length of the random password to 15 characters. | ||
/maxpass | Sets the maximum length of the random password to 256 characters. | ||
/crypto {DES-CBC-CRC|DES-CBC-MD5|RC4-HMAC-NT|AES256-SHA1|AES128-SHA1|All} | Specifies the keys that are generated in the keytab file:
Note The default settings are based on older MIT versions. Therefore, /crypto should always be specified. | ||
/itercount | Specifies the iteration count that is used for AES encryption. The default is that itercount is ignored for non-AES encryption and set at 4,096 for AES encryption. | ||
/ptype {KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL|KRB5_NT_SRV_INST|KRB5_NT_SRV_HST} | Specifies the principal type.
| ||
/kvno <KeyVersionNum> | Specifies the key version number. The default value is 1. | ||
/answer {-|+} | Sets the background answer mode: - Answers reset password prompts automatically with NO. + Answers reset password prompts automatically with YES. | ||
/target | Sets which domain controller to use. The default is for the domain controller to be detected, based on the principal name. If the domain controller name does not resolve, a dialog box will prompt for a valid domain controller. | ||
/rawsalt | Forces Ktpass to use the rawsalt algorithm when generating the key. This parameter is not needed. | ||
{-|+}dumpsalt | The output of this parameter shows the MIT salt algorithm that is being used to generate the key. | ||
{-|+}setupn | Sets the user principal name (UPN) in addition to the service principal name (SPN). The default is to set both in the .keytab file. | ||
{-|+}setpass <Password> | Sets the user's password when supplied. If rndpass is used, a random password is generated instead. | ||
/?|/h|/help | Displays command-line Help for Ktpass. |
Remarks
Services running on systems that are not running the Windows operating system can be configured with service instance accounts in Active Directory Domain Services. This allows any Kerberos client to authenticate to services that are not running the Windows operating system by using Windows KDCs.
The /princ parameter is not evaluated by Ktpass and is used as provided. There is no check to see if the parameter matches the exact case of the userPrincipalName attribute value when generating the Keytab file. Case sensitive Kerberos distributions using this Keytab file might have problems when there is no exact case match and could fail during pre-authentication. Check and retrieve the correct userPrincipalName attribute value from a LDIFDE export file. For example:
Examples
The following example illustrates how to create a Kerberos .keytab file, machine.keytab, in the current directory for the user Sample1. (You will merge this file with the Krb5.keytab file on a host computer that is not running the Windows operating system.) The Kerberos .keytab file will be created for all supported encryption types for the general principal type.
To generate a .keytab file for a host computer that is not running the Windows operating system, use the following steps to map the principal to the account and set the host principal password:
Use the Active Directory User and Computers snap-in to create a user account for a service on a computer that is not running the Windows operating system. For example, create an account with the name Sample1.
Use Ktpass to set up an identity mapping for the user account by typing the following at a command prompt:
Note
You cannot map multiple service instances to the same user account.
Merge the .keytab file with the /Etc/Krb5.keytab file on a host computer that is not running the Windows operating system.